Barran Press
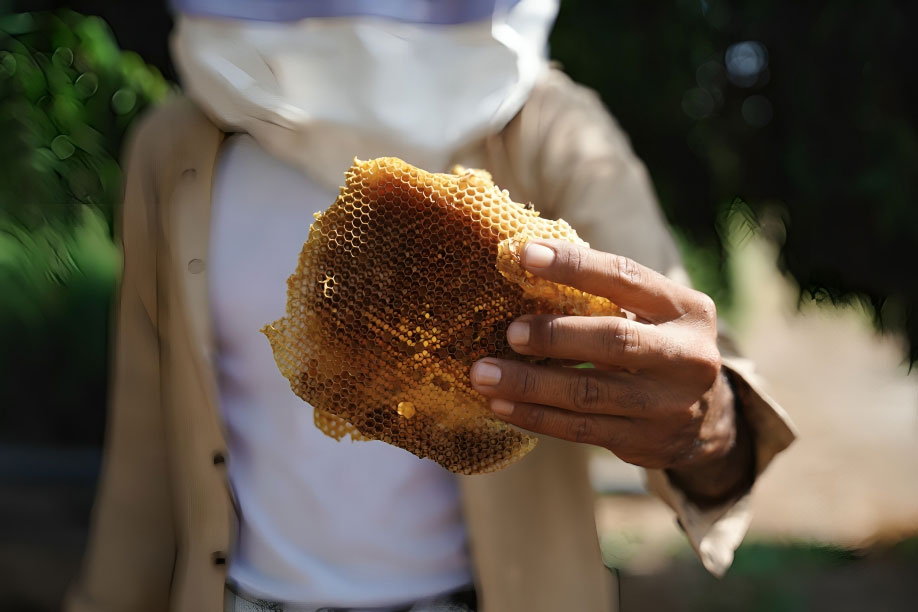
A recent study published on December 15, 2024, reveals that honey production and exports in Yemen have plummeted by up to 50% over the past five years due to climate change, rising temperatures, and the impacts of the ongoing conflict instigated by the Houthi movement.
Conducted on behalf of the International Committee of the Red Cross, the study indicates that in hotter regions of Yemen, the number of bee colonies has declined by 10-15% during the last five years. The war has exacerbated this decline, leading to more than a 50% drop in honey production and exports. Years of armed conflict, violence, and economic hardships have left the population struggling to adapt, pushing essential services to the brink of collapse.
The study highlights that beekeeping is not only vital for food security in Yemen but also serves as a source of income for approximately 100,000 families. Climate change is significantly impacting beekeeping, causing increased heat stress and reduced honey production. Irregular rainfall and extreme heat are negatively affecting bee colonies, leading to diminished foraging opportunities and disrupted flowering cycles.
It is projected that climate change could raise temperatures in Yemen by 1.2 to 3.3 degrees Celsius by 2060, with extreme temperatures expected to rise by 3 to 7 degrees Celsius by the end of the century. Additionally, the study warns that Yemen will experience more severe weather events, including intense floods, droughts, and increased storm frequency, as noted by the Climate Center.
For beekeepers in Yemen, drought conditions and declining rainfall have become increasingly common, resulting in water scarcity, which they cite as a major local challenge for agricultural production, including beekeeping. The availability of food for bees has also seen a downward trend, as beekeepers rely on wild plants that have become increasingly scarce over the past decade. Consequently, bees are struggling to find sufficient quantities and quality of nectar.
Due to the deterioration of local water and food sources, concerns have arisen about bees expending more energy and time searching for these essential resources. According to the findings, the need for bees to forage for prolonged periods and travel longer distances leads to decreased honey production.
On the other hand, increased rainfall from climate change has resulted in more frequent severe flooding, which has devastated entire bee colonies and left beekeepers without any hives in some provinces, such as Hadhramaut and Shabwa.